Protecting the skin from the sun should be a major concern for clients of all ages. Skin care professionals need to be aware of the effects the sun can have on skin and be able to educate clients on what they can do to prevent damage before it is too late.
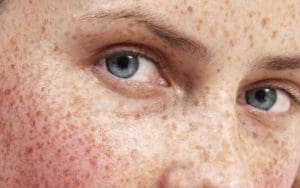
1. Preventing sun damage is much easier than restoring wrinkles. It is always easier to prevent than it is to reverse. Sun damage can cause wrinkles, discolored skin, and more serious health consequences. In some cases, once the damage is done, there is no going back.
2. Avoid deep exfoliating procedures and chemical peels during the summer. These treatments make the skin more photosensitive by removing layers of the epidermis that can act as a protective shell. The same is true for skin care products formulated with retinol, alpha hydroxyl acids, and other lightening agents. Products containing these ingredients are best used in the evening.

4. Location determines the strength of the ultraviolet rays that penetrate the skin. If clients are in the water or the snow, their safe, sun-exposure time diminishes significantly, as ultraviolet rays are reflected off the surface of snow or water.
5. The sun is most active at the equator. When traveling south, more protection is needed. Along with sunscreen, advise clients to wear protective hats and clothing to avoid serious sun damage.

7. Zinc oxide is a great active ingredient for sunscreens. It provides broad-spectrum protection by physically reflecting ultraviolet rays. It has been safely used for generations and is preferred over nanoparticles, which are not as effective.
8. Food can affect how skin responds to the sun. Processed foods with trans fats can contribute to wrinkles, skin discolorations, and other more serious conditions. Colorful, organic fruits and vegetables filled with antioxidants, like tomatoes, will support the skin during sun exposure.

10. Elevated estrogen levels and other hormonal changes often result in heightened photosensitivity. This photosensitivity can lead to hyperpigmentation. For example, melasma, the mask of pregnancy, presents as skin discoloration. Women who are taking birth control pills or who are on hormone replacement drugs may also experience similar side effects, unless they take extra measures to protect themselves from the sun.
































0 Comments