
Though a new wave of body positivity has emerged embracing women of all shapes and sizes, the sentiments surrounding cellulite are largely unchanged – it is still seen as undesirable. Store shelves are lined with products promising to diminish the appearance of dimpling. Medical spas offer treatments boasting longer-lasting results. But, will there ever be a cure?

Cellulite, which is not to be confused with cellulitis or celluloid, has been classified medically with a variety of nomenclature, including adiposis edematosa, dermopanniculosis deformans, status protrusus cutis, and gynoid lipodystrophy. The suffix ‘ite’ usually refers to inflammation in medicinal vernacular, so the term “cellulite” is technically incorrect; it is, however, widely used and accepted by physicians and the general population.
In basic terms, cellulite is the extrusion of fat pockets through layers of fascia or connective tissue just under the dermis that can be seen through the top most epidermal layer, creating skin puckering and dimpling. This effect often occurs on the hips, buttocks, and abdomen.
Cellulite occurs in most post-pubescent females and among 85 to 98 percent of women, indicating that it is physiological rather than pathological. It can result from a complex combination of factors ranging from hormones to heredity.
AESTHETIC DERMATOLOGY

Perhaps it was this new dermatological focus that brought the lumpy, bumpy skin into light. But, more likely, it is a result of the fact that the modern, western woman has been baring more skin in the past century than ever before. In fact, for the first time in a millennium, the ideal female form has moved from a voluptuous, rubenesque body type to one of slender musculature highlighting every flaw. Today, the perception of cellulite has taken on a life and treatment niche all its own.
CHARACTERISTICS

More women than men suffer from cellulite. In fact, most men show little to no sign of cellulite dimpling. Cellulite usually appears after puberty and is more prevalent in obese women. It is, however, not harmful to the body. The reason more women than men are affected by cellulite can be found in the biology of the skin and hormones. The sub-dermal collagen tissues in women are formed in rows, which allows fat to be compartmentalized and stretched back and forth, making dimpled skin and cellulite visible. The reasons for this pattern are likely due to women’s anatomical ability to stretch tissues and skin to accommodate a growing baby and widening hips. Men’s sub-dermal biology is formed in an X pattern of cells, criss-crossing the tissues to form a grid that prohibits deep pockets or dimpling of the surface skin layer.
STAGES

Without treatment or strengthening and detoxifying exercise, collagen and elastin bands begin to break down while fibrous bands wrap around clusters of fat cells instead of individual cells. This reaction creates a harder, more painful form of cellulite that can easily bruise and produce cold patches of skin where the circulation has been reduced or cut off.
CAUSES
There is increased evidence to suggest that estrogen is the most common element involved in the aggravation and persistence of cellulite. Estrogen, insulin, noradrenaline, thyroid hormones, and prolactin are part of the cellulite production process. The incidence of menstruation, pregnancy, birth control usage, and hormone replacement all seem to support this evidence.
One theory is that decreasing estrogen levels or imbalanced hormones can restrict blood flow to the connective tissue that supports the sub-dermal fat layers. Less oxygen to the tissues creates lower collagen production. Fat cells have also been shown to enlarge as estrogen levels fall.
Decreased oxygen and thinning epidermal skin (flaccidity) can result from many different factors, including age, smoking, genetics, and weight loss. Genetic factors can be linked to a person’s speed of metabolism, distribution of fat under the skin, ethnicity, and circulatory levels. Once the skin loses volume, it becomes less elastic, thinner, and more likely to sag. Underlying fat deposits will become more visible as they protrude through weakening connective tissue, resulting in a dimpling effect.
Smokers may also suffer from increased forms of cellulite. Lack of oxygen to the epidermal cells can cause a breakdown of tissue, deflating, and compression of healthy, plump cells to follow the curvature of the subcutaneous fat cells underneath.

Other sources believe a sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy eating patterns will increase one’s chances of gaining weight, escalating fat, forming cellulite earlier, or exacerbating the cellulite already present. Some studies have claimed that a toxic body alone contributes to cellulite production, but traditional medical evidence rejects this notion.
The causes that can potentially increase the appearance of cellulite include poor diet, smoking or a lack of oxygen, fad dieting, slow metabolism, lack of physical activity or sitting for long periods of time, hormone changes, dehydration, total body fat, and the thickness and color of the skin.
HOME AND SPA TREATMENTS

To date, no quick fix has been found; the most effective treatment evidence so far seems to be in the basics: exercising, eating well, and taking care of the skin and body. Furthermore, regular exercise can stimulate the body’s natural cleansing process. Through sweat and blood flow, healthier tissues can be created that hold up fat stores more easily instead of collapsing into themselves.
Topical Products
Any cream containing retinol has been shown to help with wrinkling, dimpling, and some skin indentations, but evidence supports it can never completely remove fat. Twice-daily application of a 0.3 percent retinol cream for six months can potentially thicken the skin and reduce the appearance of cellulite.
The appearance of cellulite is visibly lessened on darker skin. For those with lighter skin, self-tanner may make the bumps and dimples harder to spot. After a light body scrub, first apply self-tanner to the affected areas, then cover the rest of the body. Avoid tanning beds and natural sun exposure as ultraviolet rays will damage the skin and make cellulite more prominent.
Massage

Mechanical Massage
Endermologie (or lipomassage or endermology) is a specific type of mechanical massage. A machine with low-pressure suction kneads the skin between two spinning rollers. The theory is that the deep massage will break up the connective tissue that causes dimples and increase blood flow. Most studies show that massage techniques, including endermologie, will improve the skin’s appearance for a short time, but offer no long-term benefit. Some experts worry that the suction can cause the skin to slacken prematurely, making it look worse. The treatment is FDA-approved, but it is also pricey and may take several sessions to get results. The benefits are likely to go away without regular sessions.
Body Wraps

Ionithermie cellulite-reduction treatment focuses on reducing cellulite with ions and various topicals. The treatment claims to reduce the unpleasant appearance of cellulite while detoxifying and slimming the body. This process involves covering the affected area with micronized algae and conductive thermal aroma clay, then wrapping it in plastic before applying an electric current with attached electrodes. The treatment sessions, which take place mostly in beauty salons and spas, last for 30 minutes, but may vary depending on the size of the treatment area. According to many reviews, the treatment is not uncomfortable or painful. The results, however, are mixed and diet and exercise are recommended for best possible results.
Exercise and Diet
Get moving! It is one of the best ways to build strong muscles under those lumpy areas and make skin look more even. It does not matter what form of exercise is chosen, as cardio, walking, yoga, and weight training will improve overall body and muscle tone. Focus on the buttock and quad areas with step-ups, lunges, and squats at least twice a week for an extra cellulite-reducing boost.
Compression Wear
There are plenty of modern options for body shapers and compression workout gear. These new materials claim to hold muscles in place and improve blood flow, which may or may not help with cellulite.
MEDICAL SPA AND MEDICAL TREATMENTS
A 2015 National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) evidence-based review of 67 studies into the effectiveness of different techniques stated, “Most of the evaluated studies, including laser- and light-based modalities, radiofrequency, and others had important methodological flaws…Some evidence for potential benefit was only seen for acoustic wave therapy (AWT) and the 1440 nm Nd:YAG minimally invasive laser.”
Laser Treatments
Acoustic Wave Therapy
Also known as lipotripsy, acoustic wave therapy uses a handheld device to create sound or shockwaves to stimulate metabolic processes and improve connective tissue elasticity. This treatment promises fat reduction and body contouring. Results vary and it can take several sessions.
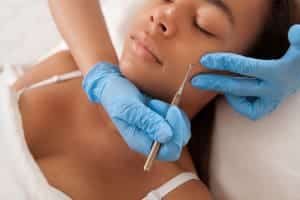
Subcision
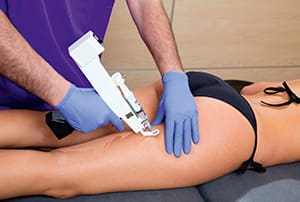
Carboxytherapy
Carboxytherapy, a non-surgical cosmetic treatment, injects gaseous carbon dioxide below the skin through a needle into the subcutaneous tissue. It claims to kill fat cells, stimulate blood flow, improve the skin’s elasticity, and reduce the appearance of cellulite. It has also become a popular treatment for stretch marks. It has not been clinically tested nor is it approved by the FDA. Side effects include bruising and mild discomfort after the procedure.
TREATMENTS TO CONSIDER CAREFULLY

Liposuction
Liposuction, also known as lipoplasty, includes laser-assisted liposuction and ultrasonic liposculpting; it is designed to remove localized pockets of fat sub-dermally through a suction tube. This procedure is ideal for people who are unable to achieve a slimmer body shape despite a healthy diet and exercise routine. This fat removal procedure is often used on the thighs, buttocks, and abdomen. Many cases, however, have proven that it can actually make the remaining dimpled fat look worse.
Cryolipolysis
This treatment is also called body shaping and claims to reduce the appearance of cellulite. This non-surgical alternative to liposuction freezes and destroys fat cells, but leaves the top skin layer intact. Within a few weeks of treatment, the dead fat cells are naturally broken down and flushed out of the body through the liver. The FDA has certified it as a safe medical treatment, but certain side effects, such as pain, swelling, and redness, affect the skin in a similar way to frostbite. In some men, hyperplasia occurred, reversing the fat cells from smaller to larger. Three treatments are recommended and may take three to four months to see results.
ON THE HORIZON
The more one looks into the condition of cellulite, the more conflicting information there seems to be. Research on cellulite and its treatments can easily be found in general medical journals. A variety of tests and diagnostics have been documented for evidence of abnormality or toxicity that would require treatment, but usually finding little-to-none.
What does seem to be prevalent for medical concern is the number of unregulated anti-cellulite treatments being performed today. Doctors and researchers repeatedly stress the importance of caution in the use of these creams and treatments and implore patients to do their homework and ask questions first.
According to the United States National Library of Medicine, “No existing treatments, including weight loss, exercise, massages, wraps, creams, supplements, or surgery, have yet been shown to get rid of cellulite. Liposuction is not recommended for cellulite, and may even make it look worse. New treatments, such as laser, are being developed for cellulite. Many people seek treatment for cellulite because they are bothered by how it looks. The problem is not harmful to your health, however. Most health care providers consider cellulite a normal condition for many women and some men.”
It is likely that dermatologists will become more interested in studying and treating this condition in the coming years and that the skin care industry may develop more effective treatments due to the increasing revenue stream. The consensus is that cellulite can never be completely removed. For now, the most effective results seem to be found through exercise, maintaining overall health and wellness, and the occasional laser or spa treatment.


























0 Comments