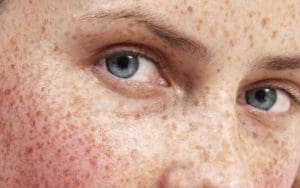
Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid with a reddish-orange pigment found in different marine algae species and wild berries, and it has demonstrated biological activity both in vitro and in vivo. It is chemically known as 3,3′-dihydroxy-β,β-carotene-4,4′-dione and has geometric and optical isomers that all exist widely in nature. Animals that consume these astanxanthin-producing organisms often exhibit a reddish-hue with some popular examples being salmon and lobster. As the compound has strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, astaxanthin has received growing interest as a valuable antiging ingredient in both nutraceuticals and cosmeceuticals.
GETTING SCIENTIFIC
When used as an ingredient in cosmetic formulations, astaxanthin may be found as a dark red powder that is soluble in lipids, fats, and other organic solvents, although the compound may be combined with plant-based polysaccharides to enhance solubility in water. The powder is generally sourced from a microalgae known as Haematococcus pluvialis, but it can be produced synthetically as well.
Want to read more?
Subscribe to keep reading this article.
Christine Tian is a research and innovation chemist at Rejuvi Laboratory. With an unwavering passion for cosmetic chemistry and product education, she is committed to advancing the boundaries of science and technology to develop cutting-edge skin care solutions. In her career, she has published papers and formulations that address the intricacies of skin health and has created products that deliver visible results. Tian has graduate degrees in cosmetic chemistry and human health, and she is dedicated to product education and delivering products that empower aestheticians to succeed in the treatment room.





























0 Comments